Structured products are financial derivative instruments that generally have a series of embedded options within them. Investors can choose a structured product based on their investment objectives and risk preferences.
These financial products can also provide investors with opportunities to access different markets and different asset classes. For example, investors can make use of various channels established by originating issuers to participate in different investments.


- Structured products can be linked to a single stock or a basket of stocks
- Structured products can be tailor-made in terms of tenors, strike prices and coupons
- Multiple stocks can be linked with one structured product
- Trading volumes of some exchange-traded derivative warrants are relatively low and if a single investor places a large trade on the open market, this may cause a wide bid-ask spread on the exchange
Raising interest rates will increase the cost of enterprises or bring uncertainties to the capital markets, but theoretically, rising interest rates are relatively favorable to the design of structured products. For example, when an investor subscribes to a structured note, the principal amount will be settled to the issuer and the issuer can earn interest income and use this income to offset a portion of the option costs inherent within structured products.
A rate hike cycle typically brings some uncertainties but at the same time there will be more principal guaranteed products to choose from in the marketplace:
(Bullish or Bearish) |
(Participation in Index Performance) |
(Early redemption) |
| Sharkfin Note | Principal Protected Note | Snowball Note |
Generally, FCNs and ELIs can be investment tools to enhance returns when investors hold relatively stable or moderately bullish views on reference stock(s). In addition to this potential interest, the payoff is determined by the performance of reference stock(s). Investors could either receive 100% of the initial principal or physical delivery of the related stock at a discounted price at maturity.
| Self-made monthly income | Strike price is generally at a discount to the current price |
When selecting the reference stock(s), investors can also consider whether the strike level is of a suitable level to cumulate the stock. In addition, please note that FCNs or ELIs can be terminated before its maturity date if the closing price of the reference stock(s) on an observation date is at or above the pre-determined early redemption price.

Click “AGREE AND CONTINUE” to confirm that you have read and understood the Important Notice and Warning Statements
Click “>” to choose ELI
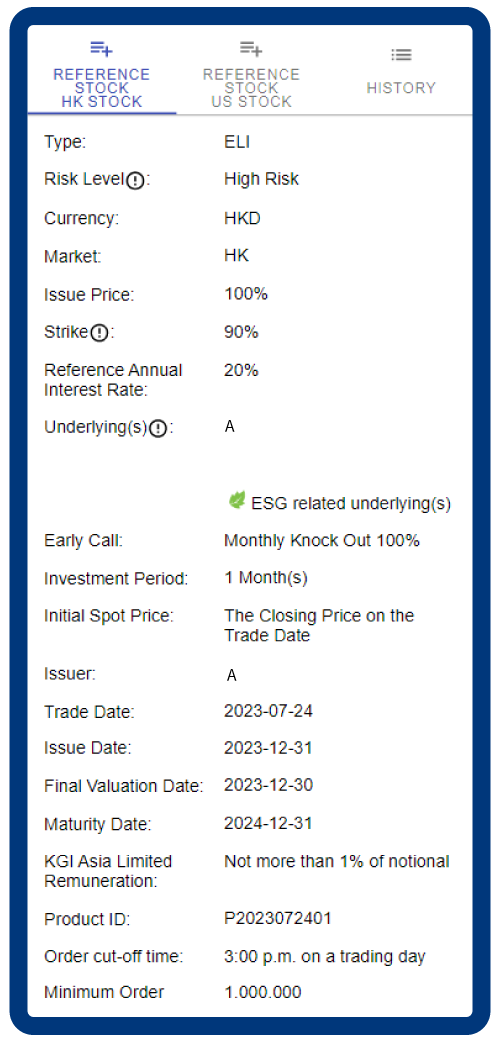
Enter “Order Nominal Amount”, check checkboxes to confirm you have read, understood and agreed to be bound by the offering documents and would accept all the risks involved in the ELI, and then click “AGREE AND CONTINUE”
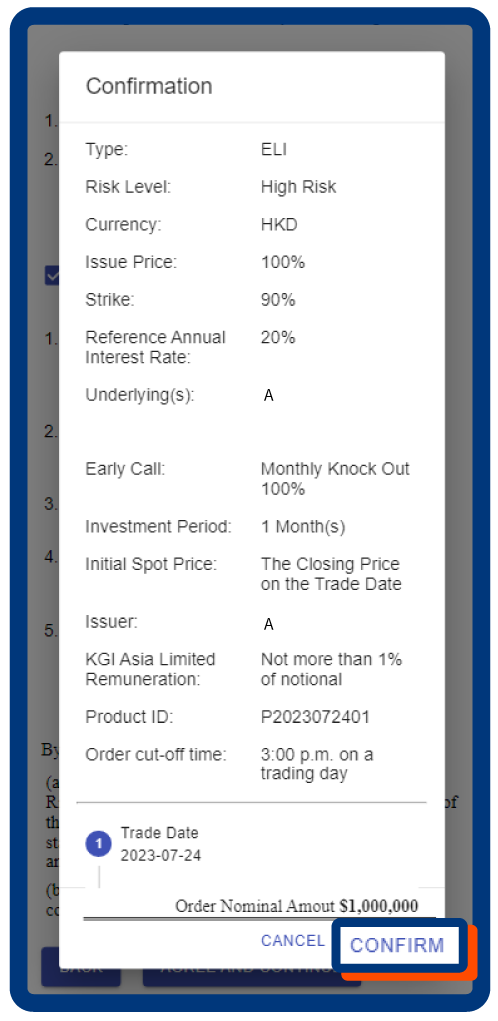
Click “CONFIRM” to submit ELI order
FCNs and ELIs are relatively easier to price because issuers incorporate the dividend factor into the pricing models.
Ordinary dividends is a foreseeable and known event, therefore issuers would include relevant factors in the quoted price of their product and no adjustments will be made on the ex-date.
As for special dividends, subdivision or consolidation of the reference stock, a bonus or rights issue, the issuer (as the calculation agent) would be acting in good faith and a commercially reasonable manner to preserve the economic equivalence of the relevant product.
Please note that all adjustments are subject to the issuer's announcement.
Volatility is the main factor in calculating the price of structured products, the increase/decrease in price is directly impacted by the level of volatility.
Investor should note that
- Volatility is not transparent, different issuers calculate it differently
- Volatility is the expectation of fluctuation in the price of the stock, not a measure of future stock movements
- Issuers will base on the implied volatility of the relevant exchange-traded and over-the-counter options, the historical volatility of the stock, and the issuer's expectation on the trend to determine the level of implied volatility
- Implied volatility only reflects the market’s expectations of stock price movements, not the direction
Structured products can be linked to stocks, exchange traded funds (ETFs), indices, futures, currencies, credits and so on.
Investors would need to be Professional Investor to subscribe FCN. General investors can subscribe ELI.
- Issuer credit risk and default risk
- The product is a derivative product, not a principal guaranteed investment product
- There is no secondary market available for this investment product at publicly available prices
If the investor would like to early terminate the investment, he can only unwind the position with the issuer, and the unwind price is determined by the issuer, with low transparency
All the information contained in this webpage is not intended for use by persons or entities located in or residing in jurisdictions which restrict the distribution of this webpage by KGI Asia Limited (“KGI”), or any affiliates of KGI. Such information shall not constitute investment advice, or an offer to sell, or an invitation, solicitation or recommendation to subscribe for or invest in any securities, insurance or other investment products or services nor a distribution of information for any such purpose in any jurisdiction. In particular, the information herein is not for distribution and does not constitute an offer to sell or the solicitation of any offer to buy any securities in the United States of America, or to or for the benefit of United States persons (being residents of the United States of America or partnerships or corporations organised under the laws of the United States of America or any state, territory or possession thereof). All the information contained in this webpage is for general information and reference purpose only without taking into account of any particular investor’s objectives, financial situation or needs and may not be redistributed, reproduced or published (in whole or in part) by any means or for any purpose without the prior written consent of KGI. Such information is not intended to provide any legal, financial, tax or other professional advice and should not be relied upon in that regard.
All investments involve risks. The prices of securities fluctuate, sometimes dramatically. The price of a security may move up or down, and may become valueless. It is as likely that losses will be incurred rather than profit made as a result of buying and selling securities.
Structured Notes are defined as a complex product. Structured notes involve derivatives.
Equity Linked Notes are structured products which are marketed to investors who want to earn a higher interest rate than the rate on an ordinary time deposit and accept the risk of repayment in the form of the underlying shares or losing some or all of their investment. When an investor purchases an Equity Linked Note, he is indirectly writing an option on the underlying shares. If the market moves as the investor expected, he earns a fixed return from his investment which is derived mainly from the premium received on writing the option. If the market moves against the investor’s view, he may lose some or all of his investment or receive shares worth less than the initial investment. Investors may lose part or all of their investment if the price of the underlying security moves against their investment view. Investors are exposed to price movements in the underlying security and the stock market, the impact of dividends and corporate actions and counterparty risks. Investors must also be prepared to accept the risk of receiving the underlying shares or a payment less than their original investment. Investors should note that any dividend payment on the underlying security may affect its price and the payback of the Equity Linked Note at expiry due to ex-dividend pricing. Investors should also note that issuers may make adjustments to the Equity Linked Note due to corporate actions on the underlying security. Investors should consult their brokers on fees and charges related to the purchase and sale of Equity Linked Note and payment / delivery at expiry. The potential yields disseminated by The Stock Exchange of Hong Kong Limited have not taken fees and charges into consideration. While most Equity Linked Note offer a yield that is potentially higher than the interest on fixed deposits and traditional bonds, the return on investment is limited to the potential yield of individual Equity Linked Note.
You are advised to exercise caution and undertake your own independent review, and you should seek independent professional advice before making any investment decision. You should carefully consider whether investment is suitable in light of your own risk tolerance, financial situation, investment experience, investment objectives, investment horizon and investment knowledge.
No representation or warranty is given, whether express or implied, on the accuracy, adequacy or completeness of information provided herein. In all cases, anyone proposing to rely on or use the information contained herein should independently verify and check the accuracy, completeness, reliability and suitability of the information. Simulations, past and projected performance may not necessarily be indicative of future results. Information including the figures stated herein may not necessarily have been independently verified, and such information should not be relied upon in making investment decisions. None of KGI, its affiliates or their respective directors, officers, employees and representatives will be liable for any loss or damage of any kind (whether direct, indirect or consequential losses or other economic loss of any kind) suffered or incurred by any person or entity due to any omission, error, inaccuracy, incompleteness or otherwise, or any reliance on such information. Furthermore, none of KGI, its affiliates or their respective directors, officers, employees and representatives shall be liable for the content of information provided by or quoted from third parties.
Members of the KGI group and their affiliates may provide services to any companies and affiliates of such companies mentioned herein. Members of the KGI group, their affiliates and their directors, officers, employees and representatives may from time to time have a position in any securities mentioned herein.
The information in this webpage has not been reviewed by the Securities and Futures Commission (“SFC”). The SFC takes no responsibility for the soundness of the authorized funds or investment products and does not imply that investment in them is recommended by the SFC.
“Complex product” refers to an investment product whose terms, features and risks are not reasonably likely to be understood by a retail investor because of its complex structure. Investors should exercise caution in relation to complex products. Investors may lose the entire invested amount or more than the invested amount (if applicable). For complex products for which the offering documents or information provided by the issuer have not been reviewed by the SFC, investors are advised to exercise caution in relation to the offer. For complex products described as having been authorized by the SFC, SFC authorization does not imply official recommendation and such authorization is not a recommendation or endorsement of a product nor does it guarantee the commercial merits of a product or its performance. Where past performance information is provided past performance is not indicative of future performance. Some complex products are only available to professional investors. Investors should read the offering documents and other relevant materials to understand the key nature, features and risks of a complex product and are advised to seek independent professional advice before making any investment decision and should have sufficient net worth to be able to assume the risks and bear the potential losses of trading the product.
Risk of trading derivative products: Trading in derivative products (including but not limited to equity-linked instruments, credit-linked notes, derivative warrants and convertible securities) tracking fluctuations in the price or level of securities, bonds, money market instruments, interest rates, reference indices or other benchmark) involves risks. Changes in market conditions may cause great changes in the value of such products. As a consequence, your related exposure to price or market risk may be significantly higher in connection with a derivative product than with other non-derivative financial instruments with which you may be familiar.
Derivative products may not be suitable for you as they can be complex and carry with them substantial risk of loss. You should make investment in derivative products only after carefully assessing among other things the direction, timing, and magnitude of the potential future changes in the price or level of the underlying asset or instrument or other benchmark, as the return of any such investment may be dependent upon such changes. However, risks associated with trading in derivative products are not and should not be presumed to be predictable. Investing in certain types of derivative products may result in your having to take or make delivery of certain underlying asset or instrument at a predetermined price. In such circumstances, you will need to perform such obligation however far the market price or level of the underlying asset or instrument has moved away from the pre-determined price or level and the resulting losses to you can be substantial.
If there is any inconsistency between the English and Chinese versions of the above Disclaimer, the English version shall prevail.

