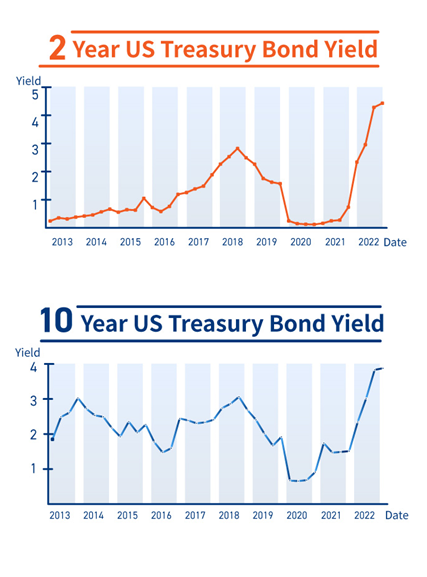

The US economy will experience a more pronounced downturn in 4Q25, which will extend into 1H26, and this will have a negative impact on consumption, slowing investment activity. Nevertheless, AI-driven productivity gains should provide some support, with US GDP growth in 2026 forecast at 2.2%.
The eurozone will see moderate growth, with Germany benefiting significantly from fiscal expansion and economic improvement. Japan’s economy will strengthen on domestic demand, aided by additional fiscal stimulus. China has demonstrated resilience under trade protectionism in 2025……

Above information as of Feb 2023


How to generate potential gains through bond investments?
Coupon Interest
Investors receive interest payments^ regularly regardless of the price movement.
Potential capital upside by capturing the price movement
Investor may also make profit by capturing price movement and trade them in the secondary market.
If investors buy the bond at a discounted price, investors may enjoy capital gain from the price difference as the bond issuer will repay the principal at par value to them at maturity.
^ Except zero coupon bonds
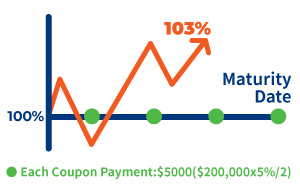
Bond Price: 103%
Bond price is higher than the par value, known as “Premium Bonds”
Yield < Coupon
Investor may sell the bond at 103% at the market, and receive accrued interest.
Your profit:
Capital Upside + Coupon received + Accrued interest
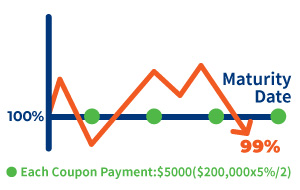
Bond Price: 99%
Bond price is lower than the par value, known as “Discount Bonds”
Yield > Coupon
There is a capital loss if you sell the bond at this level, yet it can be partially offset by the coupon and the accrued interest entitlement.
Your Profit/Loss:
Capital Downside + Coupon received + Accrued interest
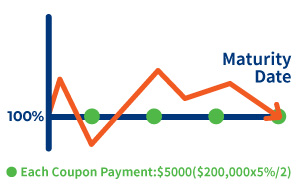
You will receive 100% of principal and last coupon payment at the maturity date.
Principal + last coupon payment = $200,000+5,000 =$205,000
Your profit::
Coupon received during your holding period
Early Redemption Feature
Callable option may be embedded in some bonds and the actual duration may be shorter than what the investors expect. As such, investor should also take the Yield to Call (YTC) into account so as to manage their expected return.
Seniority
Ranking of claim may differ from the across different in the event of default/liquidation, Claiming rank can be different for each bond even they are issued by the same entity, there can be premium for the bond with lower claim ranking.
Notes – Bond Investments
- Several credit agencies assign rating to assess their credit risk, such as Moody’s , S&P Global Ratings and Fitch.
- Bonds can be either rated as investment Grade bonds or High Yield bonds. As a nature of risk-reward, high yield bonds usually bears a higher coupon/yield than the investment grade bonds, however with higher credit risk.
- Bond issuers may not obtain credit ratings from the credit agencies.
| Moody’s | S&P Global Ratings | Fitch | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Investment Grade | Aaa Aa1 Aa2 Aa3 |
AAA AA+ AA AA- |
AAA AA+ AA AA- |
| A1 A2 A3 |
A+ A A- |
A+ A A- | |
| Baa1 Baa2 Baa3 |
BBB+ BBB BBB- |
BBB+ BBB BBB- |
|
| High Yield | Ba1 Ba2 Ba3 |
BB+ BB BB- |
BB+ BB BB- |
| B1 B2 B3 |
B+ B B- |
B+ B B- |
|
| Caa1 Ca C |
CCC CC C |
CCC CC C |
|
| In default | C | D | D |
Bonds involve default risks from the issuer. Credit ratings is not as a guarantee of the issuer’s creditworthiness.
Liquidity Risks
Investor may not sell the bonds before the maturity date as the liquidity can be limited in the secondary market for some bonds.
Interest Rate Risks
Bonds can be sensitive to the interest rate movement. There can be a negative impact on the bond price when the interest rate increases in general.
Callable Risks
Investors may face re-investment risk if the issuer redeems the bonds prior to the maturity date.
Additional risk for High Yield Bonds Investments
Credit Risks
Those bonds are usually assigned to a lower rating, or they are not rated by any credit agencies, and usually involving higher credit risk
Subject to the change of the economy cycle
There can be bigger negative impact on the high yield bonds comparing to the investment grade bonds when the economy downturns, because (i) investors may be more prudent and unwilling to bear risk exposures and (ii) higher default risks.
- Yield to Maturity (YTM) means the expected rate of return when the investor holds the bond till maturity, expressed as an annual rate of return
- Yield to Call (YTC) means the expected rate of return when the investor holds the bond till the next callable date, expressed as an annual rate of return
- Yield to Worst (YTW) means the lowest return in all possible scenarios, such the return between YTM and YTC, whichever is lower.
| 1 | Issuer | It refers to the institutions which borrow funds from the investors, they can be corporate, government or supranational bodies |
| 2 | Principal | The amount the issuer repays to the bondholder. Typically it is 100% of the face value. |
| 3 | Guarantor | Some bonds are guaranteed by the third party (as known as guarantor). In the event that the bond issuer defaults, the guarantor repays the principal and/or interest to the bondholders# |
| 4 | Ranking | Bonds can be categorized by their seniority. Some bonds are back by the collaterals, known as secured bonds. There are no collaterals for the senior unsecured bonds. In general, senior bond holders has priority compare to the subordinated bondholders for claiming. |
| 5 | Coupon | Issuer pays the bondholders at a predetermined interest rate, either fixed or variable. Some bonds bear zero percent coupon, they are normally issued at a discount price and bondholder will receive the principal in full at the maturity date. |
| 6 | Coupon Frequency | Typically, coupons are paid annually, semi-annually or quarterly. |
| 7 | Maturity | The predetermined date when the issuer repays the principal to the bondholders. Bonds with no specific maturity date are known as perpetual bonds. |
| 8 | Credit Rating | One of the consideration factors for assessing credit risks, which are assigned by the credit agencies. Generally speaking, higher credit rating will be assigned in the opinion that the bond issuer has a better capability for the repayments. |
| 9 | Accrued Interest | Investors need to pay the interest incurred between the previous coupon payment and the settlement date when the investor purchases bonds in the secondary market, apart from the principal. Investor will receive the coupon in whole if they hold the bond till the next coupon payment date. |
# Guarantors may not repay the principal and coupon in whole in the event of the issuer defaults, subject to the claiming priority and they are on case by case basis.
All investments involve risks. The prices of securities fluctuate, sometimes dramatically. The price of a security may move up or down, and may become valueless. It is as likely that losses will be incurred rather than profit made as a result of buying and selling securities.
Bond investment is NOT equivalent to a time deposit. It is NOT protected under the Hong Kong Deposit Protection Scheme. Bondholders are exposed to a variety of risks, including but not limited to: (i) Credit risk – The issuer is responsible for payment of interest and repayment of principal of bonds. If the issuer defaults, the holder of bonds may not be able to receive interest and get back the principal. It should also be noted that credit ratings assigned by credit rating agencies do not guarantee the creditworthiness of the issuer; (ii) Liquidity risk – some bonds may not have active secondary markets and it would be difficult or impossible for investors to sell the bond before its maturity; (iii) Interest rate risk – When the interest rate rises, the price of a fixed rate bond will normally drop, and vice versa. If you want to sell your bond before it matures, you may get less than your purchase price. Do not invest in bond unless you fully understand and are willing to assume the risks associated with it. Please seek independent advice if you are unsure.
You are advised to exercise caution and undertake your own independent review, and you should seek independent professional advice before making any investment decision. You should carefully consider whether investment is suitable in light of your own risk tolerance, financial situation, investment experience, investment objectives, investment horizon and investment knowledge.
No representation or warranty is given, whether express or implied, on the accuracy, adequacy or completeness of information provided herein. In all cases, anyone proposing to rely on or use the information contained herein should independently verify and check the accuracy, completeness, reliability and suitability of the information. Simulations, past and projected performance may not necessarily be indicative of future results. Information including the figures stated herein may not necessarily have been independently verified, and such information should not be relied upon in making investment decisions. None of KGI, its affiliates or their respective directors, officers, employees and representatives will be liable for any loss or damage of any kind (whether direct, indirect or consequential losses or other economic loss of any kind) suffered or incurred by any person or entity due to any omission, error, inaccuracy, incompleteness or otherwise, or any reliance on such information. Furthermore, none of KGI, its affiliates or their respective directors, officers, employees and representatives shall be liable for the content of information provided by or quoted from third parties.
Members of the KGI group and their affiliates may provide services to any companies and affiliates of such companies mentioned herein. Members of the KGI group, their affiliates and their directors, officers, employees and representatives may from time to time have a position in any securities mentioned herein.
The information in this webpage has not been reviewed by the Securities and Futures Commission (“SFC”). The SFC takes no responsibility for the soundness of the authorized funds or investment products and does not imply that investment in them is recommended by the SFC.
“Complex product” refers to an investment product whose terms, features and risks are not reasonably likely to be understood by a retail investor because of its complex structure. Investors should exercise caution in relation to complex products. Investors may lose the entire invested amount or more than the invested amount (if applicable). For complex products for which the offering documents or information provided by the issuer have not been reviewed by the SFC, investors are advised to exercise caution in relation to the offer. For complex products described as having been authorized by the SFC, SFC authorization does not imply official recommendation and such authorization is not a recommendation or endorsement of a product nor does it guarantee the commercial merits of a product or its performance. Where past performance information is provided past performance is not indicative of future performance. Some complex products are only available to professional investors. Investors should read the offering documents and other relevant materials to understand the key nature, features and risks of a complex product and are advised to seek independent professional advice before making any investment decision and should have sufficient net worth to be able to assume the risks and bear the potential losses of trading the product.
Risk of trading derivative products: Trading in derivative products (including but not limited to equity-linked instruments, credit-linked notes, derivative warrants and convertible securities) tracking fluctuations in the price or level of securities, bonds, money market instruments, interest rates, reference indices or other benchmark) involves risks. Changes in market conditions may cause great changes in the value of such products. As a consequence, your related exposure to price or market risk may be significantly higher in connection with a derivative product than with other non-derivative financial instruments with which you may be familiar.
Derivative products may not be suitable for you as they can be complex and carry with them substantial risk of loss. You should make investment in derivative products only after carefully assessing among other things the direction, timing, and magnitude of the potential future changes in the price or level of the underlying asset or instrument or other benchmark, as the return of any such investment may be dependent upon such changes. However, risks associated with trading in derivative products are not and should not be presumed to be predictable. Investing in certain types of derivative products may result in your having to take or make delivery of certain underlying asset or instrument at a predetermined price. In such circumstances, you will need to perform such obligation however far the market price or level of the underlying asset or instrument has moved away from the pre-determined price or level and the resulting losses to you can be substantial.
If there is any inconsistency between the English and Chinese versions of the above Disclaimer, the English version shall prevail.

